1.1 The Necessity and Impact of GIS based Citywide Inclusive Sanitation (G-CWIS) Training
Citywide Inclusive Sanitation (CWIS) is a public service approach that offers significant benefits in planning, designing, and implementing various ground-level sanitation interventions. CWIS involves demonstrating improved core system functions at different administrative levels to achieve and enhance the outcomes outlined under SDG 6 - Safe, equitable, and sustainable sanitation for everyone in an urban area, with special attention to the needs of the poor and marginalized groups.
The introduction of Geographic Information System (GIS) applications has provided the CWIS approach with an enriched quantitative layer to its framework, facilitating a more detailed understanding of potential interventions, even at the building footprint level as part of diverse assessment processes.
The GIS based CWIS (G-CWIS) framework not only aids in comprehending the challenges and situations at hand but also helps to understand the volume and nature of required interventions across the value chain. This insight can then be translated into both investment estimates and robust regulatory provisions.
This training has applications across all scales of city sanitation project planning and design, including components such as greywater and sewerage systems. Adoption of such innovation has proven to generate evidence-based planning and assists in optimizing the infrastructure needs for system transformations.
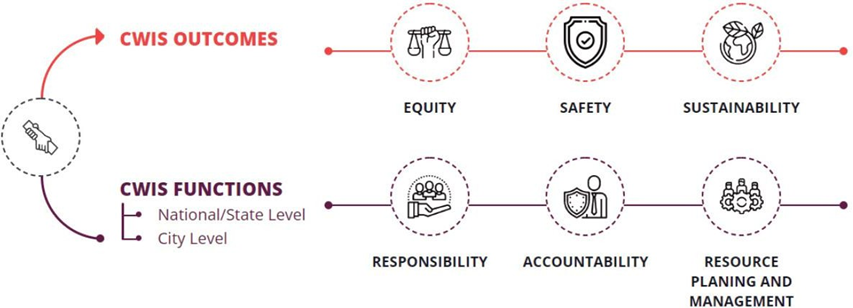
Figure 1 CWIS Service Framework
Such innovative frameworks are expected to significantly accelerate the SDG 6.2 mandate by identifying the true beneficiaries and delivering contextual sanitation solutions to safeguard against sanitation-linked public health and related issues. The G-CWIS framework has been proven and effective in answering questions like who needs to be served, where such services are required, and how they should be served. The current version of the framework, constantly improving based on project experience, has been applied in approximately 25 cities across South Asian regions, supported by BMGF and through the platform of GWSC, Thailand.
Figure 2 Need of GIS based CWIS planning applications
No Comments