1.1 Overview
The purpose of this user manual is to guide the users of IMIS on the functionalities of the web interface of IMIS. It provides detailed step-by-step procedures of all functionalities found within the IMIS web application as well as the working principle of IMIS.
The Integrated Municipal Information System (IMIS) is a comprehensive digital platform designed to transform how municipalities manage sanitation systems and services, aligning with the principles of Citywide Inclusive Sanitation (CWIS) to achieve Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 6.2. IMIS equips municipal authorities with tools to plan, monitor, and optimize sanitation service delivery, ensuring equitable access for all, particularly underserved communities. By integrating geospatial data, real-time service tracking, and sanitation-specific analytics, IMIS supports evidence-based decision-making and enhances resource allocation to improve sanitation outcomes.
IMIS also functions as a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) at the sub-national level, facilitating the generation and organization of critical data for urban sanitation management. Beyond supporting local governance, IMIS serves as a foundational data system that feeds data into national-level systems for monitoring CWIS indicators and other metrics critical for achieving sanitation targets. This capability ensures alignment between municipal operations and broader national objectives, creating a seamless flow of actionable data across governance levels.
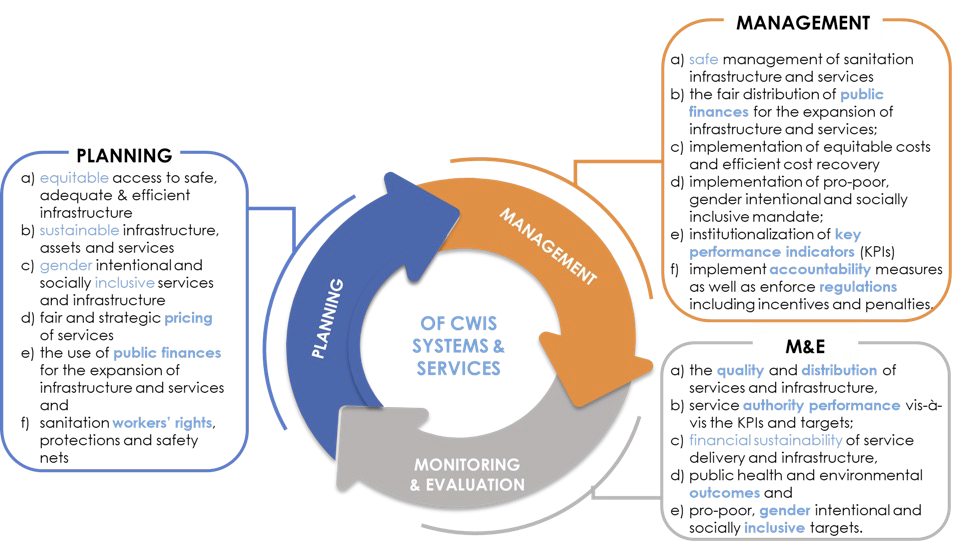
IMIS supports the Planning, Management, and Monitoring & Evaluation (M&E) framework for CWIS systems and services (see Figure 1-1). This framework emphasizes a structured approach to achieving inclusive and sustainable sanitation outcomes. The Planning component focuses on equitable and gender-inclusive strategies, sustainable financing, and transparent pricing mechanisms. The Management component ensures the safe, accountable, and financially sustainable operation of sanitation systems. The M&E component assesses service quality, equitable distribution, and the performance of sanitation authorities. Together, these components create a continuous feedback loop that helps municipalities refine their strategies and align them with national sanitation goals.
Figure 1- 1 Planning, Management and Monitoring & Evaluation Framework for implementing CWIS Approach
IMIS comprises ten functional modules, seven of which are core modules directly addressing sanitation systems and services, such as faecal sludge management, sewer connections, and public toilet operations. The remaining three value-added modules enhance complementary municipal services, including property tax collection, solid waste management, and water supply billing. Combined with the Urban Management Decision Support System (UMDSS)—a powerful tool for spatial analysis, mapping, and decision-making—IMIS empowers municipalities to adopt CWIS principles while contributing to broader urban governance. Each of these modules are discussed under sub chapter “Modules”.
Built on robust open-source technologies like PHP, PostgreSQL, and OpenLayers, IMIS is made freely available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) license. This licensing ensures that municipalities and stakeholders can access, use, and adapt the system to their needs while promoting collaboration and innovation in sanitation and urban governance. Its intuitive dashboards enable municipalities to track CWIS indicators, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), and other metrics essential for sanitation management. As a sub-national data system and DPI, IMIS strengthens municipalities’ ability to achieve sanitation objectives locally while feeding reliable, standardized data into national systems for effective CWIS monitoring and governance.
No Comments